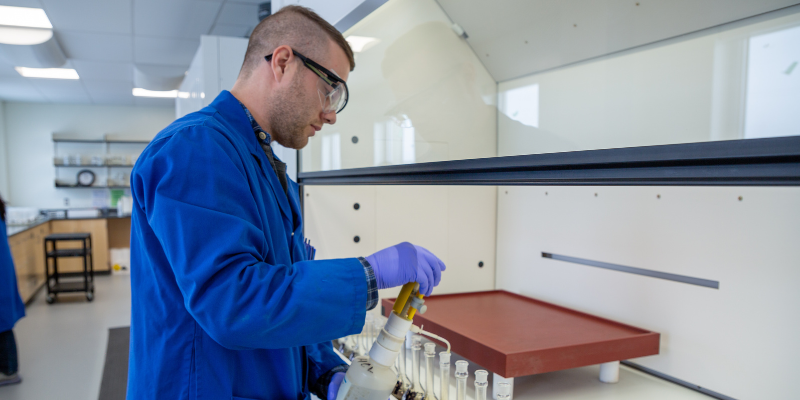
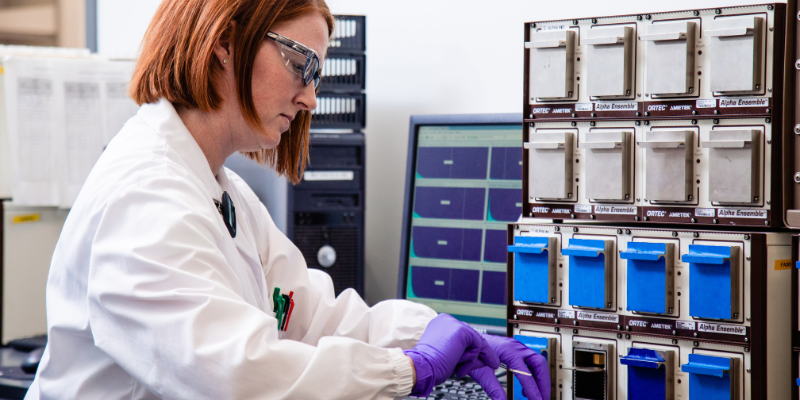
In the world of environmental testing, mineral exploration and mining, the accuracy and reliability of laboratory data are paramount. At the Saskatchewan Research Council’s (SRC) Geoanalytical Laboratories and Environmental Analytical Laboratories, our commitment to quality assurance and quality control (QA/QC) is the foundation for building trust with clients, regulators and stakeholders.
But what does a robust quality system look like in practice and, more importantly, how does it drive continuous improvement across a laboratory?
Key Points
- Quality ensures accuracy, reliability and compliance
- Data integrity is maintained through rigorous QA/QC practices
- Issues are addressed through structured reporting and corrective actions
- Continuous improvement is driven by regular audits and staff engagement
Watch our quality webinar with CIM Magazine for a more in-depth overview of QA/QC best practices, audit readiness, data integrity and continuous improvement.
Why Quality Matters
Quality is more than compliance and maintaining accreditation; when it comes down to it, it’s the backbone of operational efficiency and scientific integrity.
By adhering to ISO/IEC 17025:2017 standards and maintaining readiness for audits, SRC ensures that its results are accurate, reliable and traceable. This not only prevents incorrect results and costly rework for both the laboratory and the client, but also supports sustainable practices that protect environmental and public health.
Components of a Quality Management System

A comprehensive quality management system (QMS) integrates several key components:
- Supplier and client management
- Document and change control
- Training and competency management
- Quality event management
- Risk and audit management
- Quality Control (QC) data checks and standards
Let’s dig further into the tools in SRC’s quality toolkit.
Quality Tools in Our Laboratory Toolkit
At both SRC Geoanalytical Laboratories and Environmental Analytical Laboratories, our teams’ commitment to quality is reflected in a robust toolkit of processes and practices. Each tool plays a vital role in strengthening data integrity and supporting continuous improvement.

1. Supplier and Client Management
This tool ensures that our relationships with suppliers and clients are well-documented and transparent. By maintaining clear communication and expectations, we can trace materials and services from origin to delivery, supporting accountability and regulatory compliance.
This also allows us to perform supplier audits regularly to ensure that the suppliers we use uphold the same standards we deem crucial to our services.
2. Document and Change Control
Accurate documentation is the backbone of any quality system. Our document and change control processes guarantee that procedures, methods and records are current, accessible and properly archived. Any updates are tracked and reviewed to prevent errors and maintain consistency.
Our documents are on a regular review cycle, and experts carry out regular competency checks based upon our documented process. This ensures that our staff are performing at their best and that our documents reflect the processes happening daily in our labs.
3. Training and Competency Management
Quality results depend on skilled staff. Our training and competency management tool tracks staff qualifications, ongoing education and proficiency testing. This ensures that every team member is equipped to perform their duties to the highest standard.
Supervisors meet regularly with their team members to check in on how confident and competent they feel in their roles, and to work on growth and development in every individual.
4. Quality Event Management
When deviations or incidents occur, our quality event management tool provides a structured approach for reporting, investigating and resolving issues. This tool includes non-conformity reports (NCRs), root cause analysis and corrective actions.
Our goal with this tool is to foster a culture of transparency and learning from the lenses of positive change and continuous improvement to encourage ongoing reporting of any incidents.
5. Risk and Audit Management

Proactive risk assessment and regular audits are essential for identifying gaps and areas for improvement. Regularly identifying risks, analyzing their potential impact, tracking findings during audits and verifying the effectiveness of corrective actions allows supervisors to reinforce adherence to ISO/IEC 17025:2017 and internal SOPs. This creates an environment where identified risks can be used as opportunities to improve.
6. QC Data Checks and Standards
Data integrity is safeguarded through rigorous QC data checks. This includes the use of certified reference materials (CRMs), control charts, blanks, sample split repeats and reagent blanks. These tools help us monitor analytical performance, flag anomalies and validate our methods.
Each of the quality tools described above work together to create a resilient, responsive and continuously improving laboratory environment. By leveraging this toolkit, we ensure that our data is accurate, our processes are efficient and our clients can trust the results we deliver.
How to Ensure Data Integrity
Maintaining data integrity is an ongoing process. We employ proficiency testing programs (PTPs), certified reference materials, QC charts, blanks, sample split repeats, reagent blanks, and both internal and external audits. These tools help us monitor performance, flag anomalies and validate our analytical methods.
Quality Tools for Data Integrity: A Closer Look at Laboratory Data Checks and Balances
Maintaining data integrity in the laboratory is a continuous process, supported by a suite of specialized quality tools. Each plays a unique role in ensuring our laboratories’ analytical results are accurate, reliable and defensible.
1. Proficiency Testing Programs (PTPs)
PTPs are structured assessments where our laboratory test results are compared against predefined standards or results from peer laboratories. By participating in these programs, we validate our testing capabilities, demonstrate regulatory compliance and benchmark our performance.
PTPs provide reliable feedback loops and help us identify areas for improvement, fostering a culture of continuous development.
2. Certified Reference Materials (CRMs)
CRMs are well- characterized substances with known compositions and uncertainty values (the range that the true value is expected to fall within), accompanied by a certificate of analysis. We use CRMs to calibrate instruments, validate analytical methods and ensure ongoing quality control.
Their strategic placement in analytical runs helps monitor accuracy and detect any drift or bias in the process. It’s important that we have CRMs in every group and at regular intervals to track performance.
3. Quality Control (QC) Charts
QC charts are visual tools that track the performance of analytical processes over time. By plotting control sample results against established limits (such as ±2 and ±3 standard deviations from the mean), we can quickly detect trends, shifts or outliers.
QC charts help us flag anomalies early and take corrective action before they impact data quality.
For examples of QC charts, watch our webinar.
4. Blanks
Blanks are samples that contain no analytes of interest and are used to detect contamination or background signals. Method blanks (processed alongside real samples) and reagent blanks (containing only reagents) help us identify sources of contamination at every stage, from sample preparation to final analysis. This ensures that reported results reflect true sample composition.
5. Sample Split Repeats (SSR)
SSR involves dividing a sample (split in crushing) into multiple subsamples and analyzing them separately. This assesses the homogeneity of the sample and the consistency of the analytical process.
By comparing results from split samples, we can confirm that our methods yield reproducible and reliable data.
6. Reagent Blanks
Reagent blanks are used to check for contamination introduced by chemicals or instrumentation. By analyzing blanks that contain only reagents, we can isolate and address issues that may arise from the analytical workflow itself, ensuring that our results are not skewed by external factors.
7. Internal and External Audits
Audits are systematic reviews of our laboratory processes, records and compliance with standards such as ISO/IEC 17025:2017. Internal audits are conducted by trained staff to identify gaps, reinforce adherence to SOPs and standards, and support staff training, while external audits by accrediting bodies verify our compliance with accreditation requirements.
Findings from both types of audits lead to corrective actions and process enhancements, driving continuous improvement and operational excellence.
Together, these data integrity quality tools form a comprehensive system for monitoring performance, flagging anomalies and validating our analytical methods. By leveraging this toolkit, we uphold the highest standards of data integrity and deliver results our clients can trust.
Responding When Things Go Wrong

Even with robust systems, deviations can occur. Our Non-Conformity Report (NCR) process ensures that any issues, whether identified internally or by clients, are documented, analyzed and resolved.
Root cause analysis, corrective and preventive actions, and follow-up checks on the effectiveness of these actions are all part of our commitment to transparency and improvement.
Building a Culture of Quality
Quality is everyone’s responsibility. By encouraging open reporting of non-conformities, hosting quality seminars and including quality discussions in all meetings, we foster a culture where continuous improvement is valued and supported.
At SRC Geoanalytical Laboratories and Environmental Analytical Laboratories, we believe that a strong QA/QC program is essential for delivering high-quality results and supporting the success of our clients in the environmental, mining and mineral exploration industries.
If you have questions about our quality processes or would like to meet us at an upcoming event, please email us.

